
A motherboard (sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, planar board or logic board) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) found in computers and other expandable systems. It holds many of the crucial electronic components of the system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals.
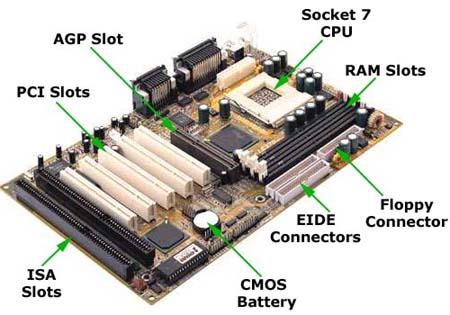
Motherboard Components
CPU - Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU) is the hardware within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system.
A computer can have more than one CPU; this is called multiprocessing. All modern CPUs are microprocessors, meaning contained on a single chip. Some integrated circuits (ICs) can contain multiple CPUs on a single chip; those ICs are called multi-core processors.

Main Memory / RAM
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a form of computer data storage. A random-access device allows stored data to be accessed directly in any random order.
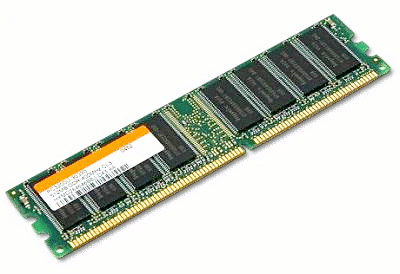
There are two different types of RAM:
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
The two types of RAM differ in the technology they use to hold data, with DRAM being the more common type. In terms of speed, SRAM is faster. DRAM needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second while SRAM does not need to be refreshed, which is what makes it faster than DRAM.
BIOS- Basic Input Output System
The fundamental purposes of the BIOS are to initialize and test the system hardware components, and to load a bootloader or an operating system from a mass memory device.
CMOS-Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
CMOS is a widely used type of semiconductor. CMOS semiconductors use both NMOS (negative polarity) and PMOS (positive polarity) circuits. Since only one of the circuit types is on at any given time, CMOS chips require less power than chips using just one type of transistor.
Cache Memory
Cache memory is random access memory (RAM) that a computer microprocessor can access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. As the microprocessor processes data, it looks first in the cache memory and if it finds the data there (from a previous reading of data), it does not have to do the more time-consuming reading of data from larger memory.
Expansion Buses
An expansion bus provides an input/output pathway for transferring information between internal hardware, such as RAM or the CPU, and expansion devices such as a graphics card or sound card.
The different types of buses include PCI, ISA, and EISA expansion bus.
Chipset
A chipset is a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found in the motherboard of a computer. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance.

| Hardware |
| Input Devices |
| Output Devices |
| Motherboard |
| Memory |
| Storage Devices |
| Web Pages by Students |
ABC of C Language by Shailender Sharma |
Bootable Pen Drive by Avtar Singh |
e-Trash or e-Treasure? by Pallavi Bagga |
Lakshya by Rabina Bagga |
OOPs Concepts by Navjot Kaur |
Fitness First by Ankush Rathore |
Information Systems by Kajal Gupta |
Quiz Contest in C++ by Rajnish Kumar |
Core Java (Tutorial) by Shyena |
C Language Q&A by Anmol Sharma |
HTML 5 Tutorial by Kishan Verma |








