C++ Programs
C++ Programs (Algorithms)
Binary Search using Recursion
Output :-
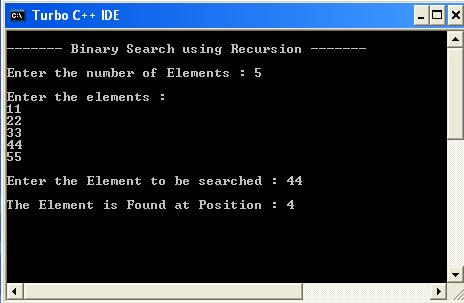

Binary Search using Recursion
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void search(int a[], int beg, int end, int item) // Function to Search Element
{
if(beg==end) // if Single Element is in the List
{
if(item==a[beg])
cout<<"\nThe Element is Found at Position : "<<beg;
else
cout<<"\nData is Not Found";
}
else
{
int mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(item == a[mid])
cout<<"\nThe Element is Found at Position : "<<mid;
else if(item < a[mid])
search(a,beg,mid-1,item); // Function Calls Itself (Recursion)
else
search(a,mid+1,end,item); // Function Calls Itself (Recursion)
}
}
void main()
{
clrscr();
int a[100],item,n,beg,end,mid,loc;
cout<<"\n------- Binary Search using Recursion -------\n\n";
cout<<"Enter the number of Elements : ";
cin>>n;
cout<<"\nEnter the elements :\n";
for(loc=1;loc<=n;loc++)
{
cin>>a[loc];
}
cout<<"\nEnter the Element to be searched : ";
cin>>item;
beg=1;
end=n;
search(a,beg,end,item); // Function Call in Main Function
getch();
}
Output :-

| Web Pages by Students |
ABC of C Language by Shailender Sharma |
Bootable Pen Drive by Avtar Singh |
e-Trash or e-Treasure ? by Pallavi Bagga |
Lakshya by Rabina Bagga |
OOPs Concepts by Navjot Kaur |
Fitness First by Ankush Rathore |
Information Systems by Kajal Gupta |
Quiz Contest in C++ by Rajnish Kumar |
Core Java (Tutorial) by Shyena |
C Language Q&A by Anmol Sharma |
HTML 5 Tutorial by Kishan Verma |









